|
|||||||
|
ss: Display Linux TCP / UDP Network and Socket Information
Время создания: 20.05.2016 22:04
Раздел: root - Linux - Console
Запись: Yurons/mytetra/master/base/1463771096j1h4kn9r8y/text.html на raw.githubusercontent.com
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Linux Tips, Hacks, Tutorials, And Ideas In Blog Format ss: Display Linux TCP / UDP Network and Socket Information The ss command is used to show socket statistics. It can display stats for PACKET sockets, TCP sockets, UDP sockets, DCCP sockets, RAW sockets, Unix domain sockets, and more. It allows showing information similar to netstat command. It can display more TCP and state information than other tools. It is a new, incredibly useful and faster (as compare to netstat) tool for tracking TCP connections and sockets. SS can provide information about:
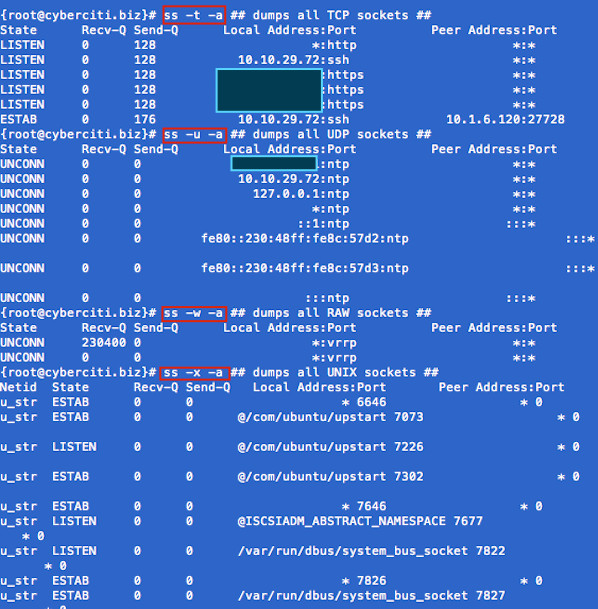
Task: Display Sockets Summary List currently established, closed, orphaned and waiting TCP sockets, enter: Total: 734 (kernel 904) TCP: 1415 (estab 112, closed 1259, orphaned 11, synrecv 0, timewait 1258/0), ports 566 Transport Total IP IPv6 * 904 - - RAW 0 0 0 UDP 15 12 3 TCP 156 134 22 INET 171 146 25 FRAG 0 0 0 Task: Display All Open Network Ports # ss -l ss -l Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port 0 0 127.0.0.1:smux *:* 0 0 127.0.0.1:10024 *:* 0 0 127.0.0.1:10025 *:* 0 0 *:3306 *:* 0 0 *:http *:* 0 0 *:4949 *:* 0 0 *:domain *:* 0 0 *:ssh *:* 0 0 *:smtp *:* 0 0 127.0.0.1:rndc *:* 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 *:* 0 0 *:https *:* 0 0 :::34571 :::* 0 0 :::34572 :::* 0 0 :::34573 :::* 0 0 ::1:rndc :::* Type the following to see process named using open socket: 0 0 *:4949 *:* users:(("munin-node",3772,5)) munin-node (PID # 3772) is responsible for opening port # 4949. You can get more information about this process (like memory used, users, current working directory and so on) visiting /proc/3772 directory: Task: Display All TCP Sockets # ss -t -a Task: Display All UDP Sockets # ss -u -a Task: Display All RAW Sockets # ss -w -a Task: Display All UNIX Sockets # ss -x -a
Fig.01: ss command in action Task: Display All Established SMTP Connections # ss -o state established '( dport = :smtp or sport = :smtp )' Task: Display All Established HTTP Connections # ss -o state established '( dport = :http or sport = :http )' Task: Find All Local Processes Connected To X Server # ss -x src /tmp/.X11-unix/* Task: List All The Tcp Sockets in State FIN-WAIT-1 List all the TCP sockets in state -FIN-WAIT-1 for our httpd to network 202.54.1/24 and look at their timers: How Do I Filter Sockets Using TCP States? The syntax is as follows:
Where FILTER-NAME-HERE can be any one of the following,
Examples Type the following command to see closing sockets:
Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port 1 11094 75.126.153.214:http 175.44.24.85:4669 How Do I Matches Remote Address And Port Numbers? Use the following syntax:
Find out connection made by remote 123.1.2.100:http to our local virtual servers: State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 0 75.126.153.206:http 123.1.2.100:35710 ESTAB 0 0 75.126.153.206:http 123.1.2.100:35758 How Do I Matches Local Address And Port Numbers?
How Do I Compare Local and/or Remote Port To A Number? Use the following syntax:
Where OP can be one of the following:
Examples
ss command options summery
ss vs netstat command speed Use the time command to run both programs and summarize system resource usage. Type the netstat command as follows: real 2m52.254s user 0m0.178s sys 0m0.170s Now, try the ss command: real 2m11.102s user 0m0.124s sys 0m0.068s Note: Both outputs are taken from reverse proxy acceleration server running on RHEL 6.x amd64. Recommended readings:
Why haven’t I heard of the ‘ss’ command before? This is great – I’ve tested the commands on several servers and this will be an excellent addition to the tools I’ve already been using. Thanks for bringing this command to the light of day for me! :) REPLY LINK astonishing. years of unix administration and never stumbled across this goodie? REPLY LINK OK, where the HECK is this thing? REPLY LINK It is part of iproute package. The source code can be obtained from: REPLY LINK ss -4nlp cheers ! REPLY LINK Yummy, thanks for sharing! And ss is included in CentOS 5.2. Best, REPLY LINK Thanks for sharing this great tool. I’m loving it. REPLY LINK Good job and it is really helped me a lot REPLY LINK I really appreciate you guys for sharing your knowledge of linux commands for admin type of commands that come in handy for checking out your network and activity, and open tools for open ports.once again thanks. REPLY LINK These are some great tools. Thanks for keeping up posting the stuff I need to get things done. REPLY LINK In the last speed tests you should add -n so DNS resolving doesn’t slow down the commands. In my testing ss was at least 10 times faster than netstat. REPLY LINK Your “time” commands are unfair. Almost all of the time consumed by netstat, is consumed by doing reverse DNS lookups on every IP returned. I suggest you try the test again using “time netstat -nat”. Adding the “n” will stop the reverse DNS lookups, and the response should be nearly instantaneous. Waiting two minutes for a netstat response would drive me nuts. REPLY LINK ©2000-2016 nixCraft. All rights reserved. Privacy - Terms of Service - Questions or Comments |
|||||||
|
Так же в этом разделе:
|
|||||||

|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|