|
||||||||||||||
|
Loop Control
Время создания: 05.09.2017 00:32
Текстовые метки: knowledge
Раздел: Java - Tutorial - Syntaxis
Запись: xintrea/mytetra_db_mcold/master/base/1504560750jo7z1gbh55/text.html на raw.githubusercontent.com
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
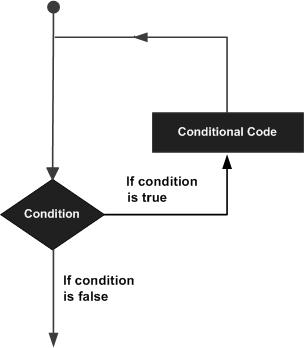
Java - Loop Control Advertisements There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on. Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths. A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times and following is the general form of a loop statement in most of the programming languages − Java programming language provides the following types of loop to handle looping requirements. Click the following links to check their detail.
Loop Control Statements Loop control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed. Java supports the following control statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
Enhanced for loop in Java As of Java 5, the enhanced for loop was introduced. This is mainly used to traverse collection of elements including arrays. Syntax Following is the syntax of enhanced for loop − for(declaration : expression) { // Statements }
Example public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; for(int x : numbers ) { System.out.print( x ); System.out.print(","); } System.out.print("\n"); String [] names = {"James", "Larry", "Tom", "Lacy"}; for( String name : names ) { System.out.print( name ); System.out.print(","); } } } This will produce the following result − Output 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, James, Larry, Tom, Lacy, |
||||||||||||||
|
Так же в этом разделе:
|
||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|